Human Resource Planning: Definition, Objectives and Steps
HR Planning is the process of using an organization’s goals and strategy to forecast the organization’s HR needs in terms of finding, developing, and keeping a qualified workforce.”
Answers the Question:
“What must we do today to be prepared for tomorrow
HRM planning is a process by which an organization ensures that it has the right number and kinds of people, at the right time, capable of effectively and efficiently completing those tasks that will help the organization to achieve its overall strategic objectives.
HRM & Organizational Strategy
- Human resource planning ultimately translates the organization’s overall goals into the number and types of employees needed to meet those goals.
- Employment planning cannot exist in isolation. It must be linked to the organization’s overall strategy.
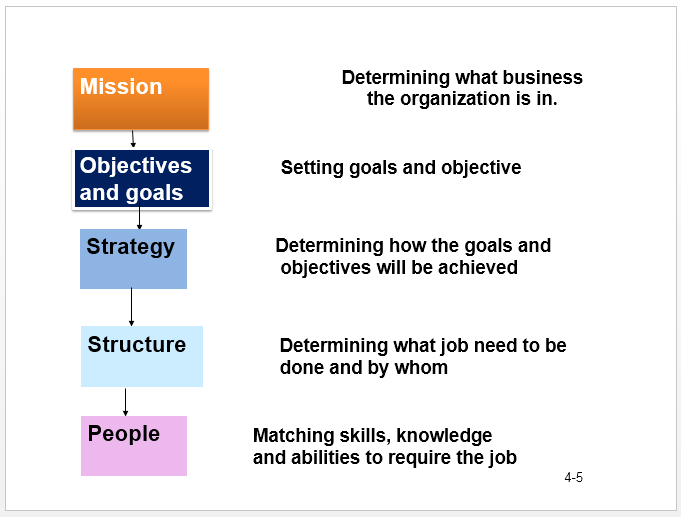
Steps to strategic human resource planning
Strategic Planning
Procedures for making decisions about the organization’s long-term goals and strategies
Strategic Human Resources Management
The pattern of human resources deployments and activities that enable an organization to achieve its strategic goals.
Strategy Formulation — providing input as to what is possible given the types and numbers of people available.
Strategy Implementation — making primary resource allocation decisions about structure, processes, and human resources.
Importance Of Human Resource Planning
Human resource planning (HRP) is the process of forecasting an organization’s future demand and supply of human resources and developing strategies to meet the needs. I would like to describe the importance of HRP. Human resource planning is essential for organizations to remain competitive. HRP provides organizations with a structured framework for strategic decision-making in areas such as recruitment and selection, career development and succession planning.
- Ensuring that the organization has the right number and types of employees with the necessary skills and experience to achieve its goals.
- Helping the organization to anticipate and respond to changes in the business environment, such as changes in technology or market conditions.
- Facilitating the effective use of human resources by aligning them with the organization’s objectives.
- Helping the organization to manage workforce diversity and address issues related to equal employment opportunity and affirmative action.
- Aiding the organization in meeting its legal and regulatory compliance requirements related to human resources.
- Reducing the risk of staff shortages or surpluses, and minimizing the costs associated with recruitment and turnover.
- Providing a framework for making decisions about human resources, such as decisions related to recruitment, training, and development.
- Contributes to achieving the overall organizational goals and objectives.
- FUTURE PERSONAL NEEDS
- Surplus or deficiency in staff strength
- Results in the anomaly of surplus labor with the lack of top executives
2. COPING WITH CHANGE
- Enables an enterprise to cope with changes in competitive forces, markets, technology, products & government regulations
3. CREATING HIGHLY TALENTED PERSONNEL
- The HR manager must use his/her ingenuity to attract & retain qualified & skilled personnel
- Succession planning
4. PROTECTION OF WEAKER SECTIONS
- SC/ST candidates, physically handicapped, children of the socially disabled & physically oppressed and backward-class citizens.
- INTERNATIONAL STRATEGIES
- Fill key jobs with foreign nationals and re-assignment of employees from within or across national borders
- FOUNDATION FOR PERSONNEL FUNCTIONS
- Provides information for designing & implementing recruiting, selection, personnel movement(transfers, promotions, layoffs) & training & development
- INCREASING INVESTMENTS IN HUMAN RESOURCES
- Human assets increase in value
- RESISTANCE TO CHANGE AND MOVE
- Proper planning is required to do this
- OTHER BENEFITS
- Upper management has a better view of the HR dimensions of business decision
- More time is provided to locate talent
- Better opportunities exist to include women & minority groups in future growth plans
- Better planning of assignments to develop managers can be done
Results of Inadequate HR Planning:
-Vacant positions create costly inefficiencies
-Overtime hours at a premium cost
-Simultaneous layoffs and hiring
-Mass layoffs requiring:
-severance pay
-extended notice periods
Ineffective training, development, and career planning
-Turnover of high performers
-Problems with employment equity goals
-Inability to meet operational and strategic plans
Factors Affecting Human Resource Planning
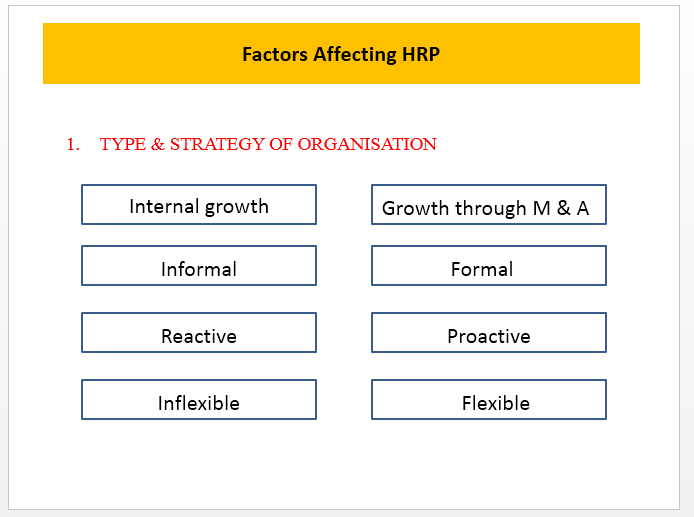
- ORGANIZATIONAL GROWTH CYCLES & PLANNING
- Embryonic/ Introduction stage – No personnel planning
- Growth stage – HR forecasting is essential
- Maturity stage – Planning more formalized & less flexible
- Declining stage – Planning for layoff, retrenchment & Retirement
III. ENVIRONMENTAL UNCERTAINTIES
- Political, social & economic changes
- Balancing programs are built into the HRM program through succession planning, promotion channels, layoffs, flexi-time, job sharing, retirement, VRS, etc….
IV.TIME HORIZONS
Short-term & Long-term plans
- TYPE AND QUALITY OF FORECASTING INFORMATION
- Type of information that should be used in making forecasts
- NATURE OF JOBS BEING FILLED
- The difference between employing a shop-floor worker & a managerial personnel
Environmental Scanning
Sources of Information
- Publication
- Professional Association
- Conferences and Seminars
- Professional Consultants
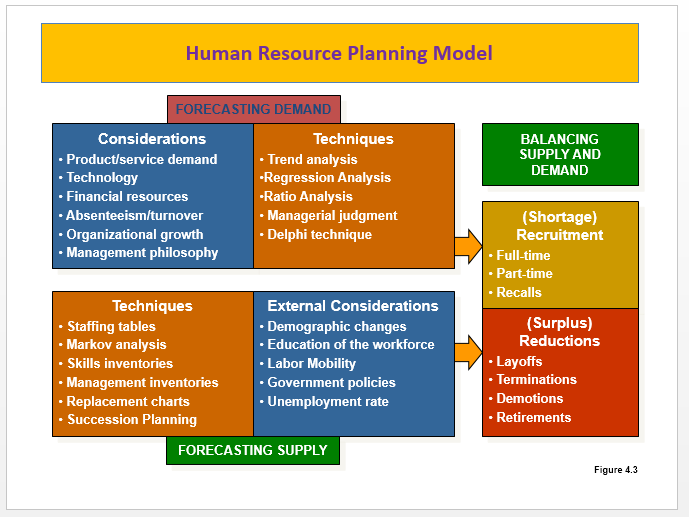
Elements of Effective HR Planning
- Forecast Future HR Needs (Demand)
- Forecast Future Internal/External Candidates (Supply)
- Implement Plans to Balance Supply and Demand
- Monitor and Evaluate Results
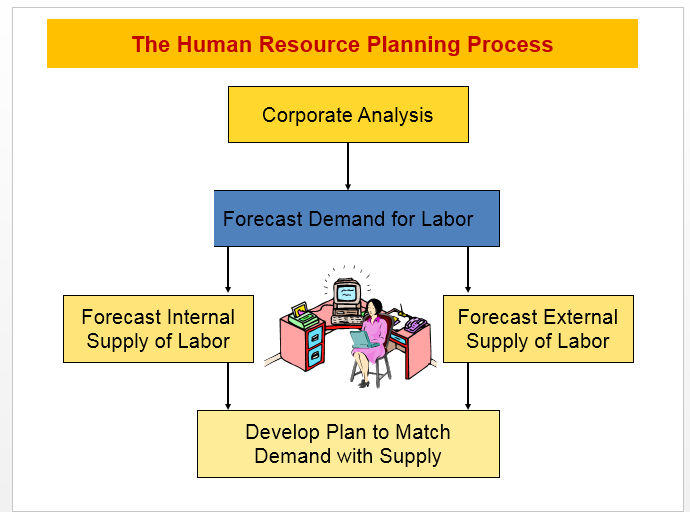
Four Phases of HR Planning
The overall process of HR planning generally occurs in four closely related phases:
- Assessing supply and demand
- Developing objectives
- Designing and implementing programs
- Evaluating outcomes
Phase 1: Assessing Supply and Demand
- Situation analysis and environmental scanning;
- Forecasting HR demands
- (Trend projection, unit-demand forecasting) ;
- Reconciling the budget;
- Forecast HR supply (skills inventory).
Phase 2: Developing Objectives
- Considering corporate strategy & goals;
- The objectives set will also depend upon the needs identified in phase 1;
- Organizational culture and employee attitudes such as commitment and customer focus.
Phase 3: Designing and Implementing Programs
- To increase the supply of certain categories of employees or to decrease the number of current employees;
- To make organizations more attractive to a broader of applicants;
- To improve the organization’s socialization efforts so that good employees want to remain with the organization;
- To downsize or ‘right-size’ the organization.
Phase 4: Evaluating Outcomes
- To quantify the value of HR;
- An HRIS facilitates the rapid and frequent collection of data;
- Data collection is important for evaluating programs and making adjustments;
- Determining the effectiveness of HR plans;
- Demonstrating the significance of planning and the HRM department itself to the organization as a whole.